Apache Kafka (Theory)
Apache Kafka is an event-streaming platform.
Info
Event records the fact that something happened in the world or in our business.
- To publish and subscribe-to
- To store streams of events durably and reliably for as long as we want
- To process streams of events as they occur
- Servers and Clients communicate via TCP network protocol
- Can be deployed on bare-metal hardware, containers, VMs, cloud env etc.
Terminologies
Producers & Consumers
- Producers/Publishers are clients who write data/events to Kafka
- Consumers/Subscribers read data/events from Kafka
- Both consumers and producers may not have knowledge of each other's existence
- Both are fully decoupled
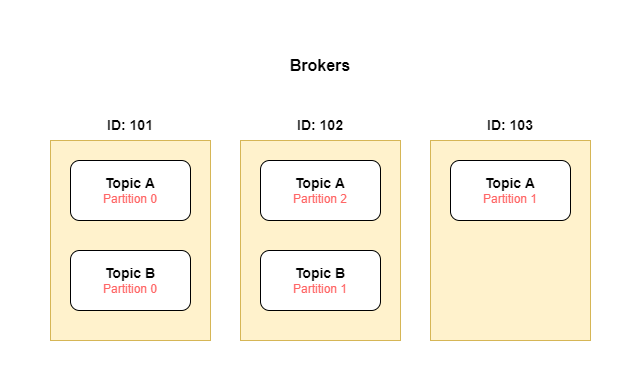
Brokers
- machines on which Apache Kafka is running and providing services to both producers and consumers
- Each system can have multiple brokers (recommended for HA and FT) and each broker can be identified by an ID
- Each broker can have one or more topic partitions and those partitions will be replicated across multiple brokers
- If the client connects to any broker, the client will be connected to the entire cluster
Topics, Partitions & Offsets
- like tables in a db
- events are organized and durably stored in topics
- topics can have multiple producers writing events and at the same time, multiple consumers consuming those events
- topics are split into partitions like 0, 1, 2, 3... etc. Each message inside the partition gets an incremental id called offset, which has meaning only in that specific partition
- Each topic has a replication factor that states how many times every partition in the topic should be replicated across different brokers (should be
>1) - If one broker goes down, another broker gets up and serves the data
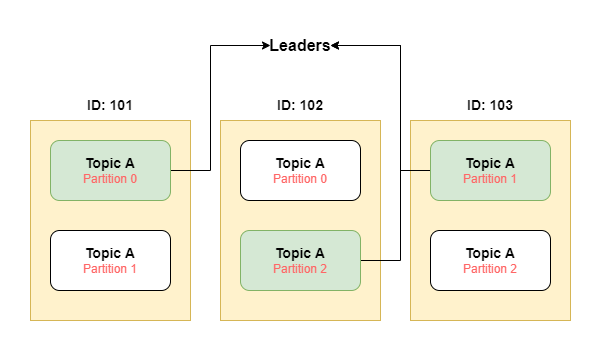
Owners
- As each partition is replicated across brokers, then who will be the owner of that partition? That's the leader.
- At any time, only One broker can be the leader for a given partition. Only that leader can receive and serve data for that partition and other brokers will synchronize data.
- In the following image, if the broker with id
101goes down, as that partition is already present on the broker with id102, then the broker with id102will be the new leader for the partition0
Important
Once data is written to a partition, it can't be changed (immutability).
Producers
- Producers write data to topics and automatically know to which broker and partition to write and in case of broker failure, producers auto-recover themselves.
- They can choose to receive acknowledgement of data writes (default is
acks=1):acks=0: no ack (possible data loss)acks=1: ack from leader only (limited loss)acks=2: leader + replicas (no data loss)
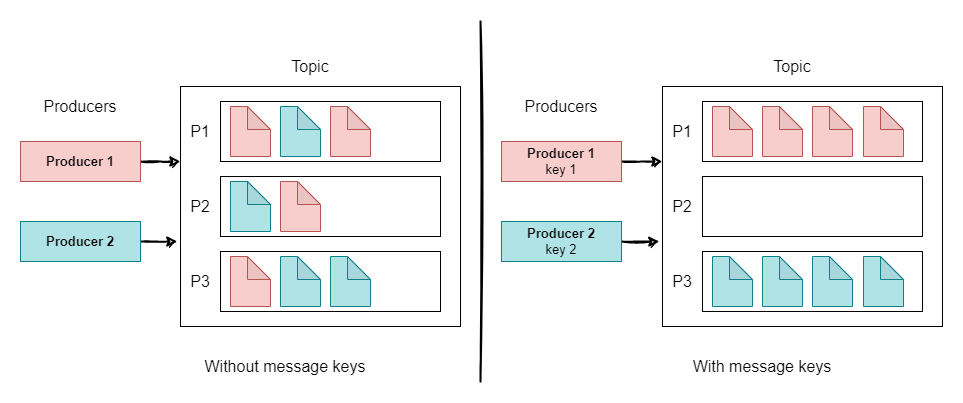
Message Keys
- Producers can also send keys with messages
Consumers
- They know which broker (leader) to read from and if a broker fails, how to recover.
- Data is read in order within each partiton.
- The same message can also be read multiple times if a consumer wants to.
Consumer Groups
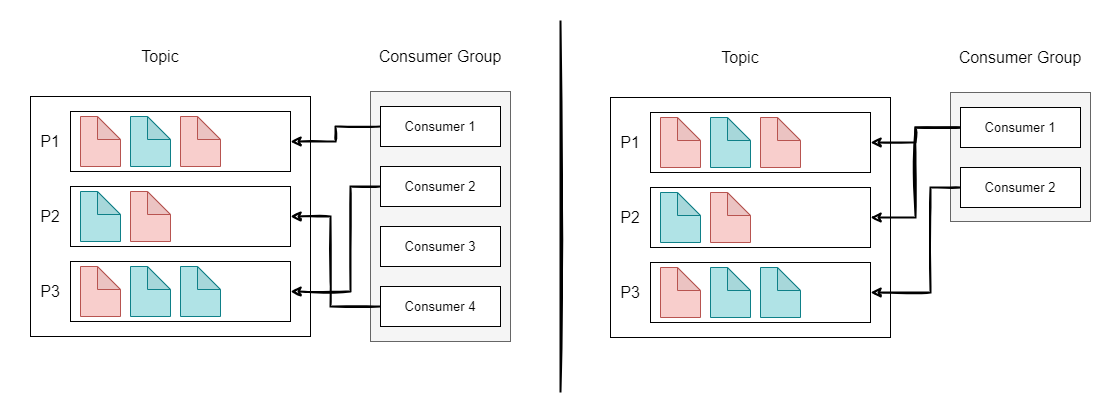
- Consumers can read data in consumer groups.
Consumer Offset
- Kafka stores the offsets at which a consumer group has been reading. It tells the consumer where it was the last time in the partition & which message to read next.
- Offsets are committed live in a Kafka Topic.
- When the consumer in the group has processed data received from Kafka, it should be committing the offsets.
- If consumers die, they will be able to read back from where it left off.
Apache Kafka Guarantees
- Messages are appended to a topic partition in the order they are sent.
- Consumers read messages in order stored in the topic partition.
- With a replication factor of
N, the producer & consumer can tolerate uptoN-1brokers being down.
Where can I use event streaming for?
- To process payments and financial transactions in real-time
- To continuously capture and analyze sensor data from IoT devices or other equipments
- To monitor patients in health care
- To serve as the foundation for data platforms, event-driven architecture, and microservices