ArgoCD
Basics
- GitOps uses Git as a single source of truth to deliver applications and infrastructure.
- ArgoCD is the tracking option.
- Simple idea is that: If our source code has a mechanism of tracking, why our deployment shouldn't have a mechanism of tracking.
GitOps Principles
- Declarative: A system managed by GitOps must have its desired state expressed declaritively.
- Versioned & Immutable: Desired state is stored in a way that enforces immutability, versoning and retains a complete version history.
- Pulled Automatically: Software agents automatically pull the desired state declarations from the source.
- Continuously Reconciled: Software agents continuously observe the actual system and apply any changes if they happen.
Other GitOps Tools
- Jenkins X
- Flux
- Spinnaker
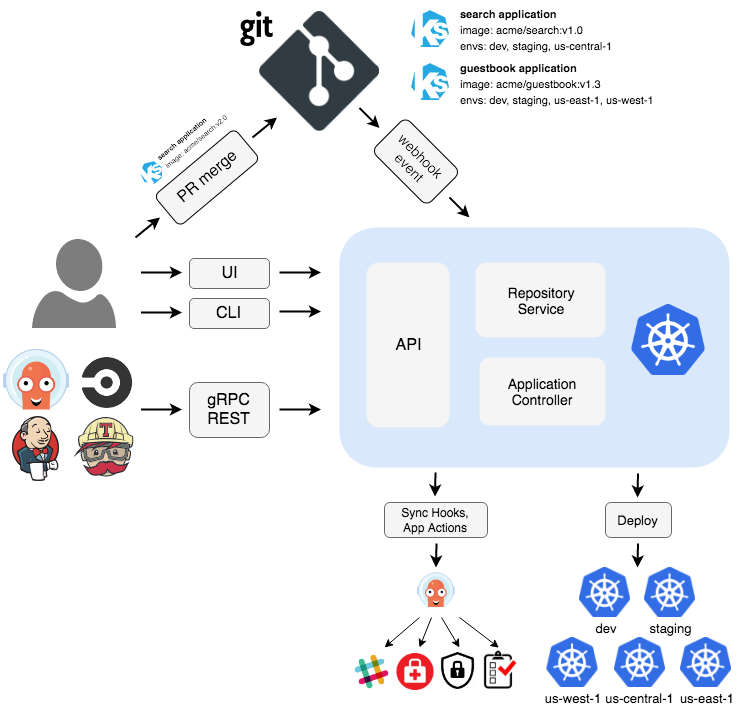
ArgoCD Architecture
In ArgoCD we have:
- Repo Server: Connect to git and get the state
- Application Controller: Talks to k8 and get the state
- UI/CLI/API Server: for user
- Dex: OIDC Provider/User Login/Proxy Server
- Redis: For caching the state
ArgoCD Setup
-
Installation & Server
-
CLI & Password change
-
Create a Deployment
Multi-Cluster Deployment
- In prod scenarios, we may have a single dedicated cluster (centralized cluster) to ArgoCD which has access to other clusters.
- GitOps says move away from the traditional CD practices like ansible, shell or python scripts as they cannot identify modifications. Rather move towards tools like ArgoCD, Flux.
- Even if the developer edits the manifest in the cluster, ArgoCD will discard the change and bring back to the original state as specified in the single source of truth: the Git.
- Hub-Spoke Model: There is a single centralized controller which continuously scans the git and deploys to the necessary controller as required. May require High CPU & memory. May get overloaded.
- Localized Model: Each instance of ArgoCD present in each cluster. But have to manage each one of them independently.
Configuring the Cluster
- Go to
argo-cd/docs/operator-manual/argocd-cmd-params-cm.yaml. It has all the parameters that can be used in the ArgoCD configmap. - Just in testing, we edit the
argocd-cmd-params-cmconfigMap, and run as insecure by adding: - The above configmap is mounted in the
argocd-server. - If we have multiple nodes, and our pod is running on one node with NodePort config. We don't need to exec into the particular node to access the service. We can access it from any node, node1:31655, node2:31655, node10:31655,
kube-proxywill internally route the requests to that one exposed port. - To get the k8 context:
kubectl config get-contexts | grep us-east-1. - So, for adding a cluster to ArgoCD, we do:
argocd cluster add <result-from-above> --server <argo-cd-server-ip>:<port> - Then deploy in the same way that we do locally. For more, see: YouTube Video Link.